TCP MSS |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › mtu tcp › TCP MSS |
TCP MSS
|
void tcp_v4_err(struct sk_buff *icmp_skb, u32 info)
|
|-- dst = inet_csk_update_pmtu(sk, mtu);
|-- tcp_sync_mss(sk, mtu);
通信双方是如何将 mss_cache 设为一致的
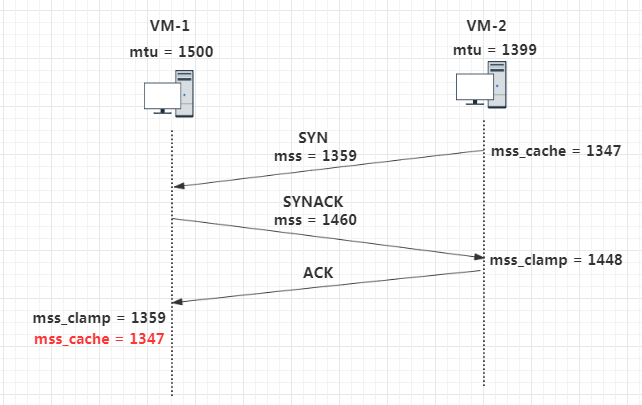
有了前面的铺垫,再来看所谓的 MSS “协商过程”就容易多了。 这里我用两台虚拟机作为 TCP 连接的双方,虚拟机网卡的默认 mtu 是 1500,而我将主动端虚拟机网卡 mtu 设置为 1399. TCP 默认开启了 timestamp 选项。 最终主动端(vm-2)和被动端(vm-1)的mss_cache都被设置成了 1347 主动端:mss_cache = 1399(mtu) - 20(IP首部) - 20(TCP首部) - 12(timestamp) = 1347 被动端:mss_cache = 1359(mss_clamp) - 12(timestamp) = 1347Linux内核源码处理ICMP packet too big与DF 结论 ICMP packet too big对ICMP packet too big的处理,TCP/UDP最终都对对应路由条目进行MTU更新。而TCP的MTU、MSS、窗口大小和最终段大小的关系比较复杂,目前没有看明白。 Don’t fragmentDF位的默认配置,受系统配置控制,Ubuntu 14.04默认开启MTU发现功能。推断结果:UDP大报文默认未置上,而TCP大报文默认置上。 Linux内核如何处理ICMP Packet too big ICMP流程 报文类型: 23 #define ICMP_DEST_UNREACH 3 /* Destination Unreachable */ 43 #define ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED 4 /* Fragmentation Needed/DF set */
if (ip_exceeds_mtu(skb, mtu)) { IP_INC_STATS(net, IPSTATS_MIB_FRAGFAILS); icmp_send(skb, ICMP_DEST_UNREACH, ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED, htonl(mtu)); goto drop; } https://kernel.googlesource.com/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/nico/archive/+/24497521076f7ce46c176d2dad018744e6f8cedd/net/inet/icmp.c iCMP差错报文的数据部分包括:原始数据报的IP首部再加上前8个字节的数据部分(2字节源端口+2字节目的端口+4字节序号) icmp_send(skb,ICMP_DEST_UNREACH, ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED, dev->mtu, dev); icmp_send(struct sk_buff *skb_in, int type, int code, struct device *dev) { struct sk_buff *skb; struct iphdr *iph; int offset; struct icmphdr *icmph; int len; DPRINTF((DBG_ICMP, "icmp_send(skb_in = %X, type = %d, code = %d, dev=%X)\n", skb_in, type, code, dev)); /* Get some memory for the reply. */ len = sizeof(struct sk_buff) + dev->hard_header_len + sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct icmphdr) + sizeof(struct iphdr) + 8; /* amount of header to return ,8 字节*/ skb = (struct sk_buff *) alloc_skb(len, GFP_ATOMIC); if (skb == NULL) return; skb->sk = NULL; skb->mem_addr = skb; skb->mem_len = len; len -= sizeof(struct sk_buff); /* Find the IP header. */ iph = (struct iphdr *) (skb_in->data + dev->hard_header_len); /* Build Layer 2-3 headers for message back to source. */ offset = ip_build_header(skb, dev->pa_addr, iph->saddr, &dev, IPPROTO_ICMP, NULL, len, skb_in->ip_hdr->tos,255); if (offset < 0) { skb->sk = NULL; kfree_skb(skb, FREE_READ); return; } /* Re-adjust length according to actual IP header size. */ skb->len = offset + sizeof(struct icmphdr) + sizeof(struct iphdr) + 8; icmph = (struct icmphdr *) (skb->data + offset); icmph->type = type; icmph->code = code;//mtu值,传给对方 icmph->checksum = 0; icmph->un.gateway = 0; memcpy(icmph + 1, iph, sizeof(struct iphdr) + 8); // 8字节,包含传输层源端口和目的端口 icmph->checksum = ip_compute_csum((unsigned char *)icmph, sizeof(struct icmphdr) + sizeof(struct iphdr) + 8); DPRINTF((DBG_ICMP, ">>\n")); print_icmp(icmph); /* Send it and free it. */ ip_queue_xmit(NULL, dev, skb, 1); }
icmp_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb),根据ICMP类型处理skb: icmp_pointers[icmph->type].handler(skb);icmp_pointers的定义显示,ICMP_DEST_UNRAECH的handler为icmp_unreach,后者获取出ICMP头部的mtu后,投递给icmp_socket_deliver(skb, mtu)。icmp_socket_deliver最终将skb和mtu值投递给ipprot->err_handler(skb, info); /* Handle ICMP_UNREACH and ICMP_QUENCH. */ static void icmp_unreach(struct icmphdr *icmph, struct sk_buff *skb) { struct inet_protocol *ipprot; struct iphdr *iph; unsigned char hash; int err; err = (icmph->type code; iph = (struct iphdr *) (icmph + 1); switch(icmph->code & 7) { case ICMP_NET_UNREACH: DPRINTF((DBG_ICMP, "ICMP: %s: network unreachable.\n", in_ntoa(iph->daddr))); break; case ICMP_HOST_UNREACH: DPRINTF((DBG_ICMP, "ICMP: %s: host unreachable.\n", in_ntoa(iph->daddr))); break; case ICMP_PROT_UNREACH: printk("ICMP: %s:%d: protocol unreachable.\n", in_ntoa(iph->daddr), ntohs(iph->protocol)); break; case ICMP_PORT_UNREACH: DPRINTF((DBG_ICMP, "ICMP: %s:%d: port unreachable.\n", in_ntoa(iph->daddr), -1 /* FIXME: ntohs(iph->port) */)); break; case ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED: printk("ICMP: %s: fragmentation needed and DF set.\n", in_ntoa(iph->daddr)); break; case ICMP_SR_FAILED: printk("ICMP: %s: Source Route Failed.\n", in_ntoa(iph->daddr)); break; default: DPRINTF((DBG_ICMP, "ICMP: Unreachable: CODE=%d from %s\n", (icmph->code & 7), in_ntoa(iph->daddr))); break; } /* Get the protocol(s). */ hash = iph->protocol & (MAX_INET_PROTOS -1); /* This can change while we are doing it. */ ipprot = (struct inet_protocol *) inet_protos[hash]; while(ipprot != NULL) { struct inet_protocol *nextip; nextip = (struct inet_protocol *) ipprot->next; /* Pass it off to everyone who wants it. */ if (iph->protocol == ipprot->protocol && ipprot->err_handler) { ipprot->err_handler(err, (unsigned char *)(icmph + 1), iph->daddr, iph->saddr, ipprot); } ipprot = nextip; } skb->sk = NULL; kfree_skb(skb, FREE_READ); }
TCP流程 tcp_v4_err(skb, info),调用tcp_v4_mtu_reduced(struct sock *sk) 更新路由的MTU,inet_csk_update_pmtu(struct sock *sk, u32 mtu)找到路由inet_csk_rebuild_route(sk, &inet->cork.fl);更新路由MTU dst->ops->update_pmtu(dst, sk, NULL, mtu); tcp_v4_err,如果MTU变小,且可分片,则会tcp_sync_mss(struct sock *sk, u32 pmtu)。关于TCP的MSS与MTU相关的内容很多: 1274 /* This function synchronize snd mss to current pmtu/exthdr set. 1275 1276 tp->rx_opt.user_mss is mss set by user by TCP_MAXSEG. It does NOT counts 1277 for TCP options, but includes only bare TCP header. 1278 1279 tp->rx_opt.mss_clamp is mss negotiated at connection setup. 1280 It is minimum of user_mss and mss received with SYN. 1281 It also does not include TCP options. 1282 1283 inet_csk(sk)->icsk_pmtu_cookie is last pmtu, seen by this function. 1284 1285 tp->mss_cache is current effective sending mss, including 1286 all tcp options except for SACKs. It is evaluated, 1287 taking into account current pmtu, but never exceeds 1288 tp->rx_opt.mss_clamp. 1289 1290 NOTE1. rfc1122 clearly states that advertised MSS 1291 DOES NOT include either tcp or ip options. 1292 1293 NOTE2. inet_csk(sk)->icsk_pmtu_cookie and tp->mss_cache 1294 are READ ONLY outside this function. --ANK (980731) 1295 */ case ICMP_DEST_UNREACH: if (code > NR_ICMP_UNREACH) goto out; if (code == ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED) { /* PMTU discovery (RFC1191) */ /* We are not interested in TCP_LISTEN and open_requests * (SYN-ACKs send out by Linux are always sk_state == TCP_LISTEN) goto out; tp->mtu_info = info; if (!sock_owned_by_user(sk)) { tcp_v4_mtu_reduced(sk); } else { if (!test_and_set_bit(TCP_MTU_REDUCED_DEFERRED, &tp->tsq_flags)) sock_hold(sk); } goto out; }
/* * This routine reacts to ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED mtu indications as defined in RFC1191. * It can be called through tcp_release_cb() if socket was owned by user * at the time tcp_v4_err() was called to handle ICMP message. */ void tcp_v4_mtu_reduced(struct sock *sk) { struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk); struct dst_entry *dst; u32 mtu; if ((1 sk_state) & (TCPF_LISTEN | TCPF_CLOSE)) return; mtu = tcp_sk(sk)->mtu_info; dst = inet_csk_update_pmtu(sk, mtu); if (!dst) return; /* Something is about to be wrong... Remember soft error * for the case, if this connection will not able to recover. */ if (mtu < dst_mtu(dst) && ip_dont_fragment(sk, dst)) sk->sk_err_soft = EMSGSIZE; mtu = dst_mtu(dst); if (inet->pmtudisc != IP_PMTUDISC_DONT && ip_sk_accept_pmtu(sk) && inet_csk(sk)->icsk_pmtu_cookie > mtu) { tcp_sync_mss(sk, mtu); /* Resend the TCP packet because it's * clear that the old packet has been * dropped. This is the new "fast" path mtu * discovery. */ tcp_simple_retransmit(sk); } /* else let the usual retransmit timer handle it */ }
* 目的不可达、源端被关闭、超时、参数错误这四种类型 * 的差错ICMP报文,都是由同一个函数icmp_unreach()来处理的, * 对其中目的不可达、源端被关闭这两种类型ICMP报文 * 因要提取某些信息而需作一些特殊的处理,而另外 * 一些则不需要,根据差错报文中的信息直接调用 * 传输层的错误处理例程。参见 iCMP差错报文的数据部分包括:原始数据报的IP首部再加上前8个字节的数据部分(2字节源端口+2字节目的端口+4字节序号) */ void tcp_v4_err(struct sk_buff *icmp_skb, u32 info) { struct iphdr *iph = (struct iphdr *)icmp_skb->data; struct tcphdr *th = (struct tcphdr *)(icmp_skb->data + (iph->ihl type; const int code = icmp_hdr(icmp_skb)->code; struct sock *sk; struct sk_buff *skb; __u32 seq; __u32 remaining; int err; struct net *net = dev_net(icmp_skb->dev); /* * 检测ICMP报文长度是否包含了原始IP首部和原始IP数据包中 * 前8字节数据,如果不完整则返回 */ if (icmp_skb->len < (iph->ihl daddr, th->dest, iph->saddr, th->source, inet_iif(icmp_skb)); } UDP流程 __udp4_lib_err(struct sk_buff skb, u32 info, struct udp_table udptable)ipv4_sk_update_pmtu(struct sk_buff skb, struct sock sk, u32 mtu),也是基于路由更新MTU。__ip_rt_update_pmtu ping报文的处理也是类似,见ping_err。 Linux内核对DF的默认处理经阅读代码,发现控制DF标志的地方主要有两处: inet_sock.pmtudisc sk_buff.local_df以关键字pmtudisc和local_df做全局字符串搜索,发现对pmtudisc和local_df有赋值的地方很少。如下各小节分析。 另附:IP MTU DISCOVER相关宏 90 /* IP_MTU_DISCOVER values */ 91 #define IP_PMTUDISC_DONT 0 /* Never send DF frames */ 92 #define IP_PMTUDISC_WANT 1 /* Use per route hints */ 93 #define IP_PMTUDISC_DO 2 /* Always DF */ 94 #define IP_PMTUDISC_PROBE 3 /* Ignore dst pmtu */IP报文发送出口 源代码:ip_queue_xmit和__ip_make_skb,后者用于UDP。 382 if (ip_dont_fragment(sk, &rt->dst) && !skb->local_df) 383 iph->frag_off = htons(IP_DF); 384 else 385 iph->frag_off = 0; 248 int ip_dont_fragment(struct sock *sk, struct dst_entry *dst) 249 { 250 return inet_sk(sk)->pmtudisc == IP_PMTUDISC_DO || 251 (inet_sk(sk)->pmtudisc == IP_PMTUDISC_WANT && 252 !(dst_metric_locked(dst, RTAX_MTU))); 253 } AF_INET协议族 inet_create,依赖ipv4_config配置。该配置体现在/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_no_pmtu_disc,目前Ubuntu 14.04上默认ip_no_pmtu_disc=0,即由每个路由确定。 374 if (ipv4_config.no_pmtu_disc) 375 inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_DONT; 376 else 377 inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_WANT; 系统配置 可用sysctl命令配置,或通过/etc/sysctl.conf配置文件配置ip_no_pmtu_disc值,最终体现在/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_no_pmtu_disc。源码链接。 ICMP报文默认创建ICMP sk时,不发送DF报文。icmp_sk_init(struct net *net)。 PS:ICMP报文不超过576字节的限制在icmp_send接口中有体现。
TCP的MTU Probe和MSS(1) TCP的MTU Probe和MSS(2) linux tcp mtu探测
|
【本文地址】